Abnormally high expression of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) is closely related to tumor immune escape and is an important target of tumor immunotherapy. In-depth research on the structure and mechanism of action of IDO1 has promoted the discovery of many novel inhibitors. This article reviews the disclosed IDO1 inhibitors in recent years, and summarizes their potential therapeutic applications.
The Mechanism of IDO1
When APO-IDO1 binds to heme containing ferric iron, IDO1-Heme (Fe3+) is formed. In order to start the catalytic cycle, reductants are required to activate the enzyme, leaving the iron ion in the heme in a reduced ferrous (Fe2+) state. IDO1-Heme (Fe2+) combines with oxygen, and ferrous ions are oxidized to iron ions, and then combined with L-tryptophan to form a tertiary reaction complex. The second and third positions of the indole ring in tryptophan react with oxygen atoms to obtain TRP epoxides. After the ring-opening reaction, n-formylated canurine (NFK) is formed. IDO1-Heme (Fe2+)-NFK releases NFK, and regenerates IDO1-Heme (Fe2+) into the catalytic cycle.
Inhibitors That Target the Sa Site of Holo IDO1
1. Tryptophan/Indole Analogue
Early on, many tryptophan or indole analogues were identified as IDO1 inhibitors. In 2016, a series of indole derivatives were reported as IDO1 inhibitors by virtual screening, with 3-aryl indole derivative 9 showing moderate inhibitory activity (hIDO1 IC50=7μM).
Other indole analogues have also been developed as IDO1 inhibitors. An indired-based hydroxyindole derivative 12 was reported as an IDO1/TDO dual-target inhibitor (hIDO1 Ki=1μM, hTDO Ki=4μM). Subsequently, a series of 3-substituted indole derivatives, including compound 13 (hIDO1 IC50=0.19μM, MDA-MB-231IDO1 IC50=0.33μM), have also been reported to exhibit submole-level IDO1 inhibitory activity.
2. Imidazole/Triazole Analogues
4PI, a known heme binding agent, was reported in 1989 to have weak IDO1 inhibition efficacy (hIDO1 IC50=48μM). Increasing rigidity by reducing the rotatable bonds of molecules is a common strategy to improve the binding affinity and effectiveness of small molecule inhibitors.
Based on the lead compound 4PI, imidazo isoindoles tricyclic compounds are designed as IDO1 inhibitors, developed by NewLink Corporation.
3. Derivatives of N- Hydroxyamidine
The O atom of the N-hydroxyamidine derivative can coordinate with heme iron, and the halophenyl group and its side chain occupy pockets A and B, respectively. But compound 30 has a unique way of binding with the N atom of oxime group combined with heme iron. Researchers use calculations to optimize the binding pattern of IDO1 30 and propose that N-hydroxyamidines are readily bound to heme by deprotonated oxygen atoms. It is speculated that the potential metabolites of N-Hydroxyamidine derivatives may have a more significant role in tumor inhibition.
Inhibitors That Target APO IDO1
Most of the inhibitors targeting APO-IDO1 are discovered by HTS and these inhibitors have low cellular IC50 values (ranging from nanomoles to picomoles).
Recently, GlaxoSmithKline has identified a new class of IDO1 inhibitors with spiropiperidine-chroman structure. And Merck has reported the discovery of heme competitive inhibitors 45 and 46 with strong cellular activity and enhanced PK properties (HeLa IDO1 IC50=9.2nM, hWBu IDO1 IC50=22nM).
Multifunctional Polymer
IDO1 inhibitors have limited efficacy as a single agent to treat tumors, and the development of multi-drug combinations or multi-target inhibitors may provide a breakthrough in this regard.
For instance, through click reaction, IDO inhibitor compound 1 and quinone IDO/TDO inhibitor are linked to natural tubulin inhibitor CA-4, and compound 56 targeting IDO1/TDO and tubulin (anticancer target) is obtained, which can inhibit tumor growth and induce T cell activation and proliferation.
Other IDO1 Inhibitors
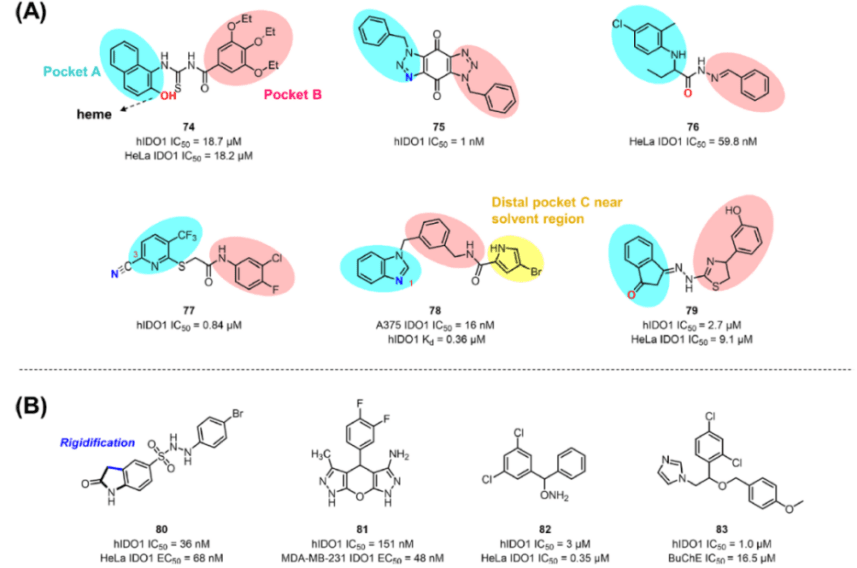
Other IDO1 Inhibitors, such as β-naphthol compound 74 and compound 75, are obtained by virtual screening and show micromole level activity in enzyme and cell tests (hIDO1 IC50=18.7μM, HeLa IDO1 IC50=18.2μM).
Several antifungal drugs, including miconazole, have been regarded as potential IDO1 inhibitors. In a follow-up study, miconazole derivative 83 is reported as a dual inhibitor of IDO1 and BuChE (hIDO1 IC50=1.0μM, BuChE IC50=16.5μM), which provides a reference for the application of the “old drug, new use” strategy in IDO1 inhibitor discovery.
Conclusion
IDO1 is the first and rate-limiting step of the catalytic Trp-Kyn pathway. It can induce immunosuppression through local tryptophan consumption and accumulation of downstream metabolites. IDO1 inhibitors are considered as potential therapeutic agents for a variety of diseases, including cancer (e.g., melanoma, lung cancer, bladder cancer), neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Huntington’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease), and viral infections (e.g., HIV). In recent years, researchers have focused on the development of small molecule IDO1 inhibitors with diverse chemical frameworks (e.g., Trp analogues, N-hydroxyamidines, etc.) and conducted in-depth studies on their inhibition mechanisms (e.g., Trp/O2- competitiveness, heme competitiveness). Most IDO1 inhibitors summarized in this article are discovered through structural-based drug design (SBDD), with the initial lead compound usually coming from HTS, VS, or natural products. The discovery and development of IDO1 inhibitors has become a research hotspot in the field of tumor immunotherapy, and it is believed that more achievements will be made in the future.
Related Targets:
| Targets | Description |
| TDO | Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase (TDO), an unrelated hepatic enzyme catalyzing the first step of tryptophan degradation. |
| IDO | IDO, also referred to indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, is an enzyme that plays a role in suppressing the immune system through catalyzing the oxidative cleavage of Tryptophan. |
Related Products:
| Name | CAS | Synonyms | Description |
| L-Tryptophan | 73-22-3 | H-Trp-OH; L-Tryptophane; L-Tryptohan | L-Tryptophan is an essential amino acid and a precursor to both serotonin and melatonin. |
| Miconazole | 22916-47-8 | NSC 169434; NSC169434; NSC-169434; Daktarin IV | Miconazole is an imidazole antifungal agent that is usually applied topically to the skin or to mucous membranes to cure fungal infections. |





