
RAS is one of the most common oncogenes found in cancer patients, with RAS mutations detected in approximately 21% of all cancers. The RAS family comprises three subtypes: KRAS, NRAS, and […]

cGAS/STING Innate Immune Signaling cGAS (cyclic GMP-AMP synthase) is a nucleotide transferase consisting of an unstructured, non-conserved N-terminal (130-150 residues) and a C-terminal containing an Mab21 domain and a highly […]

Apoptosis Definition: Apoptosis refers to a highly organized, gene-controlled process in which cells actively undergo death. It plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis and eliminating damaged, aging, or […]
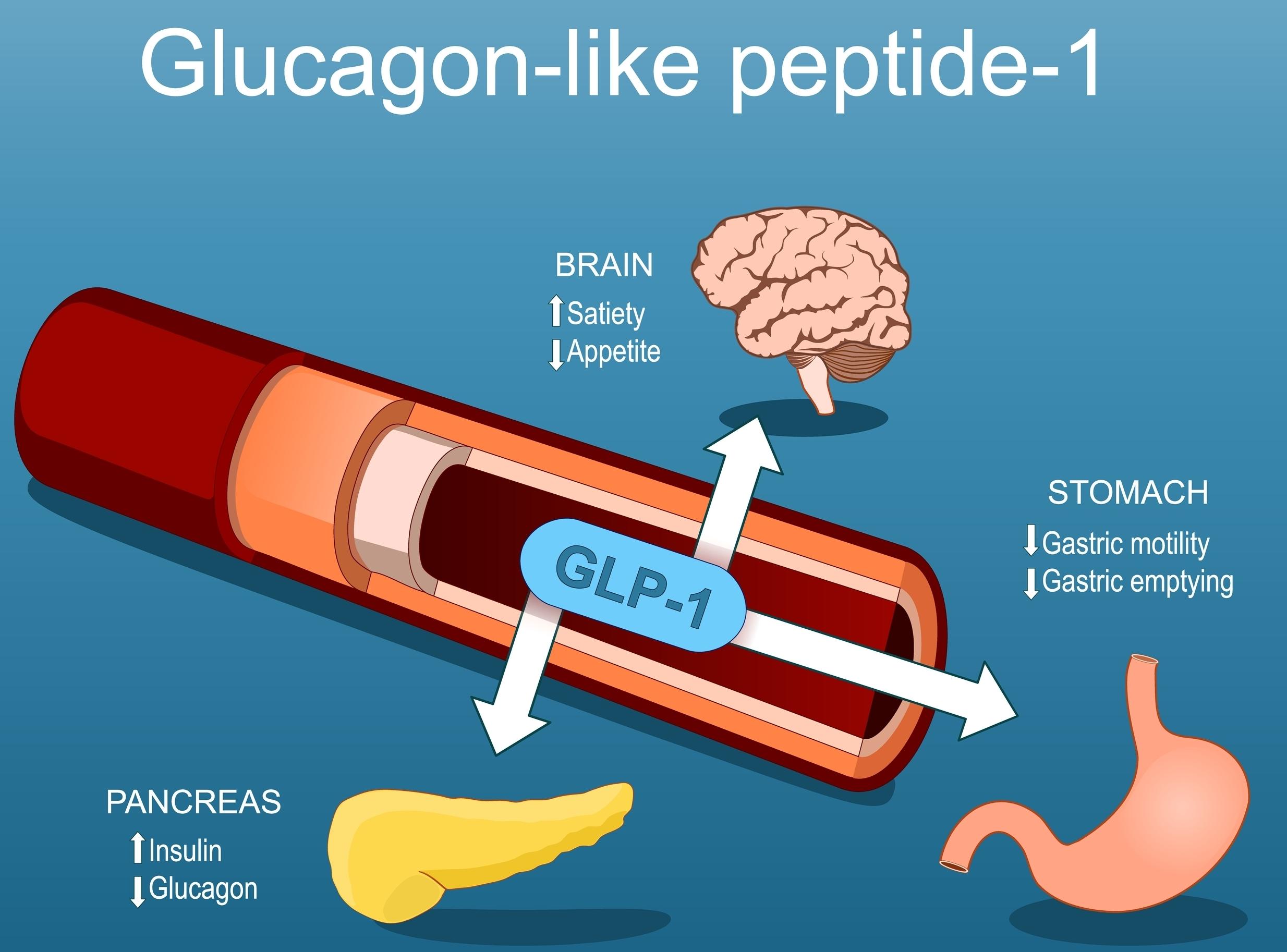
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an incretin hormone secreted by intestinal L cells in response to dietary intake. Within minutes after a meal, GLP-1 is released from the L cells in the […]

For a drug to exert its effect, it must bind to the corresponding target. Drug targets mainly include enzymes, receptors, ion channels, hormones, and cytokines. Small molecules that bind to […]

Covalent inhibitors generally refer to irreversible covalent inhibitors; however, in detailed studies, they can be divided into irreversible covalent inhibitors (ICIs) and reversible covalent inhibitors (RCIs). Advantages of covalent inhibitors […]

CD137/4-1BB combination therapy

In recent years, antibody therapies (including traditional antibodies and nano-antibodies) have become an important means of treating a wide range of human malignant diseases, and more than 100 antibody therapies […]

FDA approved the marketing of 14 drugs in the third quarter of 2023, including 6 small molecule drugs. This article mainly focuses on the drug design ideas of small molecule drugs, hoping […]

With the rise of genomics and proteomics, many clinically significant targets have been discovered in human diseases. However, a relatively small proportion of traditional druggable targets exists, and many targets […]
